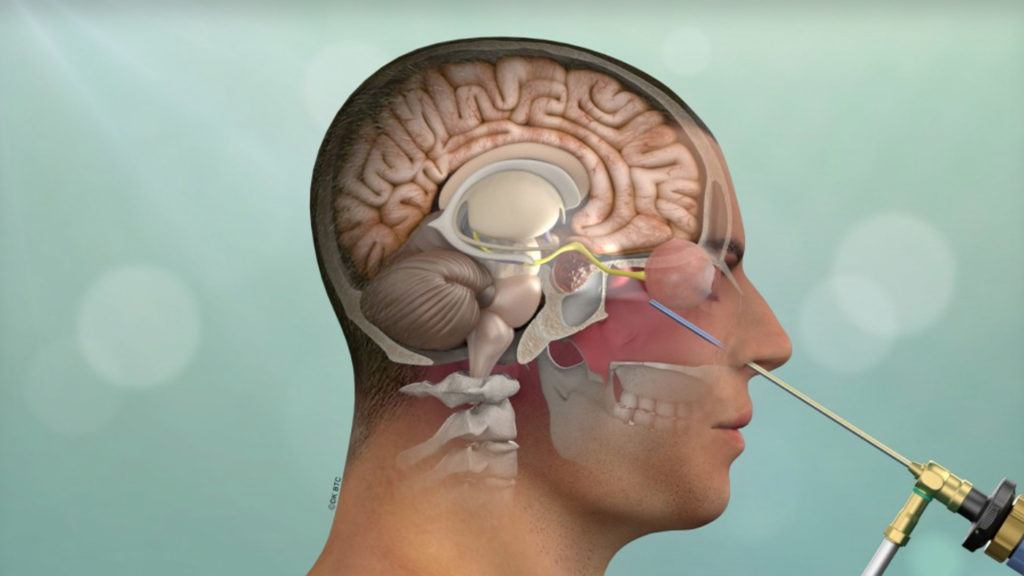
The Role Of A Brain Surgeon
Brain surgeons, or neurosurgeons, specialize in diagnosing and treating neurological conditions. They perform complex surgeries for issues like brain tumors, vascular malformations, and traumatic injuries and manage patient care from planning through rehabilitation.
Their role requires exceptional skill, a deep understanding of brain anatomy, and the ability to make critical decisions under pressure. Their expertise is crucial in managing the intricate and vital brain, significantly impacting their patients’ lives.
Types Of Neurological Challenges Treated By Brain Surgeons
Brain surgeons address a range of neurological issues:
- Brain Tumors: They carefully remove benign or malignant tumors while preserving surrounding brain tissue.
- Vascular Disorders: They treat conditions like aneurysms and arteriovenous malformations using advanced techniques.
- Other Conditions: They also handle traumatic brain injuries, spinal cord disorders, and neurodegenerative diseases, tailoring treatment to each case’s needs.
The Expertise Required For Brain Surgery
Brain surgeons require extraordinary expertise. They must deeply understand brain anatomy, including its lobes, regions, and neural pathways. This knowledge is crucial for accurate diagnosis and navigation during surgery.
They must also master advanced surgical techniques and technologies, including MRI and CT scans for detailed brain mapping and specialized instruments for minimally invasive and robotic-assisted surgeries.
Most importantly, brain surgeons must make critical decisions under intense pressure. The brain’s complexity demands precision and composure, with decisions often having life-or-death consequences.
Education And Training Of Brain Surgeons
Becoming a brain surgeon requires extensive education and training. It begins with a four-year undergraduate degree and four years of medical school, where students learn core medical disciplines.
After medical school, they complete a five to seven-year residency, gaining hands-on experience in diagnosing, treating neurological conditions, and performing surgeries.
Aspiring brain surgeons refine their skills in diagnostic imaging, treatment planning, and surgery during residency. They also develop strong communication skills for working with patients and healthcare teams.
Further specialization through fellowships is optional but allows for more profound expertise in specific neurosurgery areas. This rigorous training highlights the dedication needed to provide exceptional care.
Advanced Technology And Techniques In Brain Surgery
Brain surgery rapidly advances with new technologies and techniques, enhancing patient outcomes and minimizing risks. Brain surgeons must continually update their skills to stay at the forefront of these innovations.
Key advancements include:
- Advanced Imaging: Brain surgeons are experts in handling complex neurological conditions, using advanced tools like MRI and CT scans from Tellica Imaging for precise diagnosis and treatment. Their skills and commitment continually push the boundaries of care, adapting to new technologies and techniques to improve patient outcomes.
- Specialized Instruments: Microscopes and endoscopes are more precise, while minimally invasive techniques, like keyhole surgery, reduce patient impact and speed up recovery.
- Robotic-Assisted Surgery: Robotic systems controlled by surgeons improve precision and skill, reducing complications and enhancing outcomes.
- Innovative Techniques: Methods like awake craniotomies allow real-time brain function monitoring during surgery, reducing the risk of damage to critical areas.
These developments reflect the ongoing dedication and innovation in brain surgery, which pushes the boundaries of care and treats patients with the most advanced treatments.
Risks And Complications In Brain Surgery
Brain surgery, despite its advancements, remains complex and high-risk. Brain surgeons must be vigilant about potential complications and take steps to minimize them.
Critical Risks and Mitigation Strategies:
- Brain Damage: The brain’s delicate nature makes it susceptible to damage. Surgeons must carefully avoid harming surrounding tissue to prevent neurological deficits, such as speech, cognition, or motor function impairments.
- Bleeding and Hemorrhage: Given the brain’s high vascularization, bleeding is a significant concern. Surgeons use specialized techniques and instruments to control bleeding and manage any complications that arise.
- Infection: The risk of infection is significant due to the brain’s vulnerability to bacteria. Surgeons maintain a sterile environment and administer antibiotics to prevent post-operative infections.
- Psychological Impact: The complexity and potential outcomes of brain surgery can be daunting for patients and families. Surgeons must provide compassionate care and support throughout the process.
Despite these challenges, brain surgeons leverage advanced technology, extensive training, and a thorough understanding of brain anatomy to minimize risks and achieve the best possible outcomes.
Recovery And Rehabilitation After Brain Surgery
The journey of recovery after brain surgery is critical and involves comprehensive post-operative care. Following surgery, patients are typically moved to the intensive care unit (ICU) to closely monitor vital signs and neurological function. The brain surgeon and team adjust the treatment plan to manage complications.
Once stable, patients transition to a neurosurgical ward for specialized care and rehabilitation. This phase may include physical, occupational, and speech therapy tailored to the patient’s needs.
Rehabilitation is often a prolonged process, requiring close collaboration between the patient and their healthcare team to restore function and adapt to neurological changes. Brain surgeons provide ongoing medical management and support throughout this phase.
Addressing psychological and emotional needs is also essential. Patients may need counseling and support groups to cope with the impact of the surgery.
The success of brain surgery is measured not just by the immediate outcome but also by long-term recovery and quality of life. Brain surgeons work diligently to ensure patients regain independence and well-being through coordinated care and support.
Conclusion: The Future Of Brain Surgery
Brain surgeons’ expertise highlights the immense complexity and significance of the human brain. These professionals dedicate their careers to mastering the brain’s intricacies and are driven by a commitment to improving patient lives.
Their extensive training equips them with the skills to handle challenging neurological conditions precisely. From removing brain tumors to repairing vascular abnormalities, brain surgeons often make critical decisions that can significantly impact patient outcomes.
The field continuously evolves, with new technologies and techniques enhancing patient care and reducing risks. By embracing these advancements, brain surgeons are advancing the boundaries of what’s possible, providing hope and improved quality of life for those with neurological disorders.
As the demand for brain surgery grows with an aging population and increasing prevalence of neurological conditions, brain surgeons remain prepared to meet these challenges. Their dedication and skill ensure that the future of brain surgery continues to hold promise, driven by their expertise and commitment to patient well-being.