Physiotherapy as we know is one of branches of allied health science. The three main approaches used by physiotherapists are:
- Education and Advice
- Movement and Exercise
- Manual Therapy or Hands – on techniques
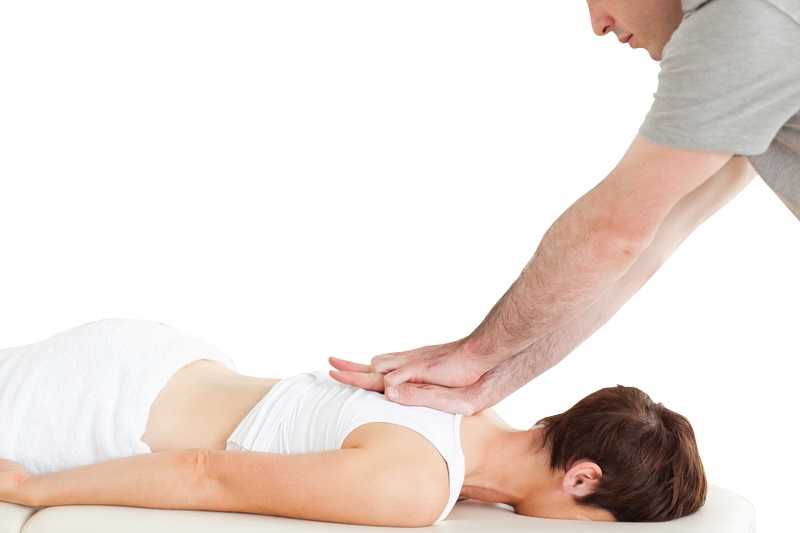
The manual therapy or Hands – on technique involves the physiotherapist to use their hands to massage, mobilise and manipulate the body tissues to provide relief from the following;
- Relieve pain and stiffness
- Improve blood circulation
- Help drain fluid efficiently from parts of the body
- Improve movement in the affected part of the body
- Promote relaxation and better quality of life
Manual therapy holds a lot of importance in physiotherapy and it is highly believed that manual therapy should be the foundation of any injury treatment in physiotherapy. Physiotherapists use sophisticated hands – on movements to treat soft tissues and joint structures. Physiotherapists kind of massage and manipulate the patient’s joints, muscles and tissues, to ascertain bio mechanical injuries, reduce the pain and facilitate proper healing.
The best thing about manual therapy is its universality, i.e. its application is not only limited to specific joints and muscles. Manual therapy can be used to treat any muscle or joint ailment right from osteoarthritis and shoulder impingement to jaw stiffness. Hence, any joint or muscle that is tensed or inflamed would surely benefit from manual therapy.
There are several different types of manual therapy techniques, that are used by a physiotherapist in accordance to the type of problem faced by the patient. The varied hands – on physiotherapy techniques are:
- Joint Mobilisation and Joint Manipulation
- Myofascial Release
- Physiotherapy Instrument Mobilisation (PIM)
- Muscle Stretching
- Neurodynamics
- Manual Traction
- Soft tissue techniques
Joint Mobilisation and Manipulation: Joint Mobilisation and Manipulation is mainly used to treat join pain and joint stiffness. Physiotherapists use high velocity movements to realign the joint and promote increased range of motion. Joint mobilisation technique varies according to the joint stiffness or hypermobility and the pain associated with moving the joint.
Myofascial Release: Myofascial Release is essentially used to relax the muscles affected by the pain and stiffness. In this technique physiotherapists stimulate the muscles to improve blood circulation and increase the flexibility of the muscle’s connective tissues.
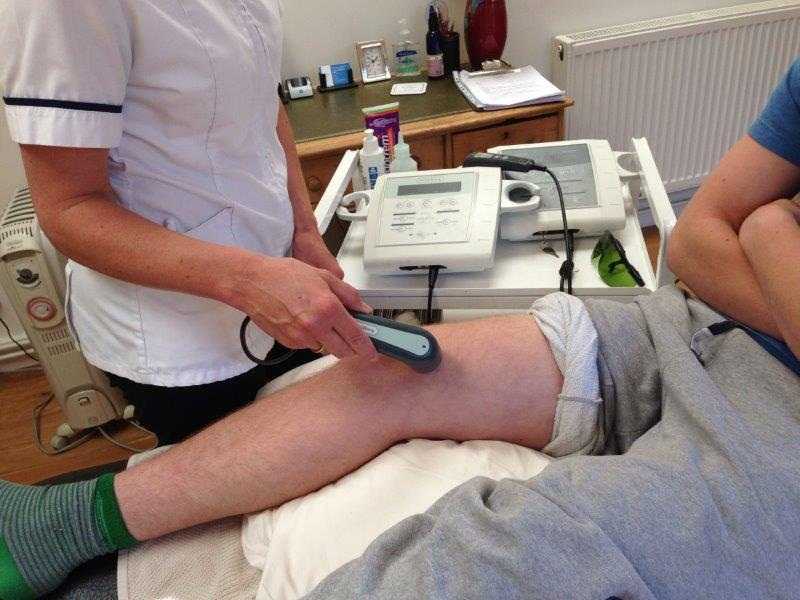
Physiotherapy Instrument Mobilisation: Physiotherapy Instrument Mobilisation involves mobilising the spinal and peripheral joints by means of a mechanical spring – loaded instrument, strictly adhering to the physiotherapy model of spinal and joint mobilisation. It is believed to offer greater reliability, specificity and safety as compared to other manual techniques.
Muscle stretching technique: The muscle stretching technique is mainly used as a corrective, preventive and recovery strategy. Muscle Stretching lengthens the muscle which often shortens during vigorous exercises thereby, facilitating greater flexibility and full range of joint movement. The different stretching exercise styles include: Static stretching, Dynamic or Ballistic stretching and Proprioceptive Neuromuscular Facilitation (PNF) Stretching.
Neurodynamics: Neurodynamics help in ascertaining which nerve has adverse neural tension and where the nerve is impeded. Neurodynamics does not involve nerve stretching rather, neurodynamics assess the structure causing nerve impediment and then treat the structure thereby, not only eliminating the nerve pain but, also facilitating the free movement of nerve.
Manual Traction: Manual Traction is basically a gentle force applied to the neck or back. This technique is mainly used to help people with problems in their discs in the cervical and lumbar spine. Manual traction relieves pressure on the spinal nerves and reduces pain, muscle spasms and muscle tension.
Soft Tissue Technique: Soft Tissue Technique is the direct physical massage on the muscle and other soft tissues of the body. This technique is basically used to target muscles, tendons, ligaments and other connective tissues like Fascia. Soft tissue technique is essentially massage of the affected area and Swedish massage and deep tissue massage are the two best known soft tissue technique.
Manual therapy or hands – on technique can vary from gentle amplitude movements barely perceived by the patient to large amplitude depending upon the type of the ailment. So, consult your physiotherapists to fix your body pain and enjoy improved flexibility and movement.
If joint or muscle pain has completely gripped you and are unable to move freely, then fret not. Simply call Portea’s at home healthcare service, to have a highly experienced and well trained physiotherapist visit you at the comfort of your home.