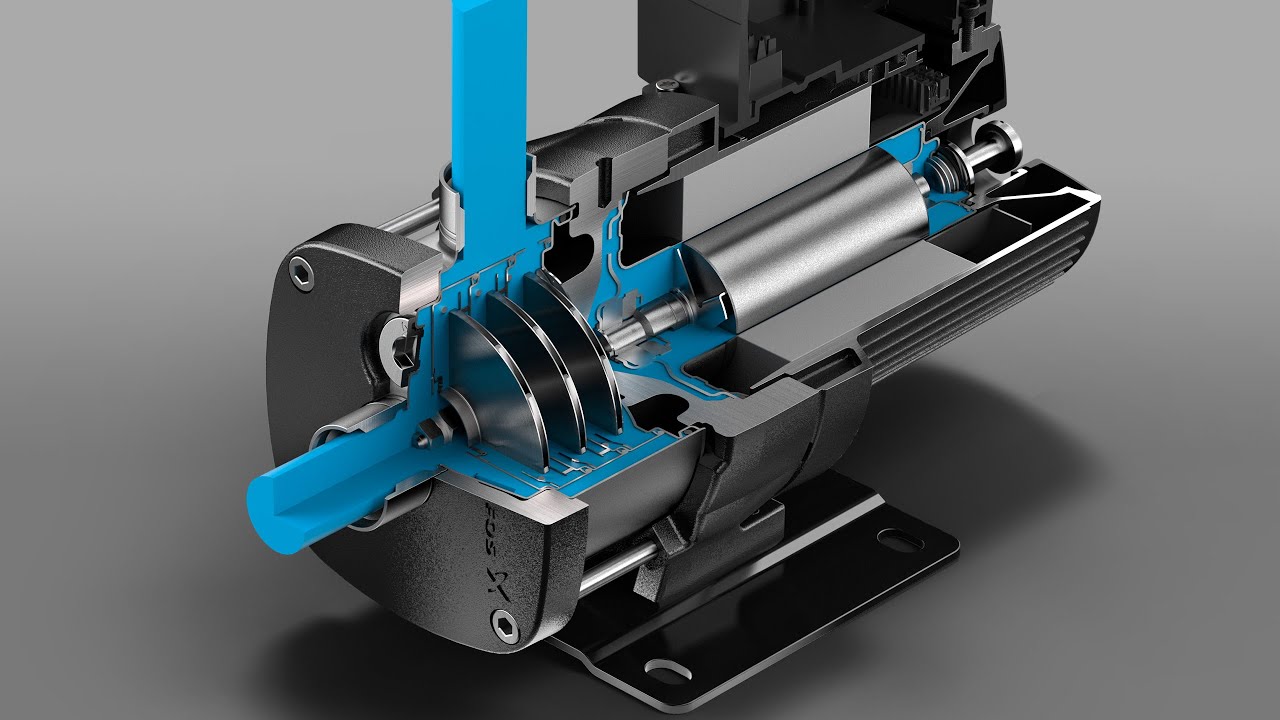
Medical pumps are essential devices in healthcare, used to deliver fluids, medications, and nutrients to patients in a controlled manner. Their precision and reliability make them indispensable in various medical settings including hospitals, clinics, and home care. This blog post will explore the different types of medical pumps, their functions, and their applications in patient care.
Types of medical pumps
There are several key types of pumps used in medical practice, each designed for specific applications:
Infusion pumps: these devices deliver fluids, such as iv fluids, medications, or nutrients, at a precise flow rate. They are crucial in settings where dosage accuracy is critical, such as in chemotherapy or neonatal care.
Volumetric pumps: common in hospital settings for delivering large volumes, controlled by a pumping mechanism that ensures consistent fluid delivery.
Syringe pumps: utilize a syringe to deliver small volumes of medication, offering very precise control over flow rates, ideal for high-stakes medications where minute quantities are crucial.
Insulin pumps: these small, computerized devices deliver insulin continuously throughout the day to diabetic patients. They mimic the way the human pancreas works by delivering insulin to the body via a catheter placed under the skin.
Enteral feeding pumps: used to deliver nutritional therapies directly into the stomach or small intestine. These are especially useful for patients who cannot eat by mouth but whose digestive systems remain functional.
Peristaltic pumps: often used in medical laboratories and some clinical settings, these pumps move fluids through tubing in a way that prevents contamination, as the fluid does not come into contact with moving parts of the pump.
Vacuum pumps: used in various medical applications, including providing suction during surgical procedures, operating sterile processing equipment, and in respiratory therapy devices to clear airways.
Applications in medical practice
The applications for medical pumps are as varied as the types of pumps themselves:
Hospital care: infusion pumps are widely used in hospitals for administering iv medications and fluids, ensuring patients receive a constant and controlled dosage. Insulin pumps are common in diabetes management, providing a continuous insulin infusion that improves blood glucose control.
Emergency medicine: in critical care and emergency settings, rapid fluid delivery can be life-saving. Volumetric pumps allow for quick administration of blood products, saline, or medications during emergencies.
Home healthcare: portable infusion pumps and enteral feeding pumps empower patients to receive necessary treatments like chemotherapy and nutritional support in the comfort of their home, improving their quality of life.
Surgical and postoperative care: vacuum pumps play a critical role in surgeries, providing necessary suction to clear surgical sites or support patient breathing.
Selecting the right pump
Choosing the right medical pump involves considering several factors:
Specific needs of the treatment: the type of fluid or medication, the required precision in delivery, and the treatment duration all influence the choice of pump.
Patient mobility: for ambulatory patients, lightweight and portable pumps are preferred.
Ease of use: devices should be user-friendly, especially for home care settings where patients or family members may be responsible for operating the pump.
Conclusion
Medical pumps are vital tools in modern healthcare, enhancing the ability to deliver treatments with precision and care. Understanding the various types of pumps and their applications helps healthcare providers make informed decisions about the best equipment for their specific medical needs, ultimately improving patient outcomes. Whether used in a hospital or at home, these pumps ensure that patients receive the treatments they need in a safe and efficient manner.